In the world of plumbing and infrastructure, selecting the right pipe material is a critical decision that can significantly impact the longevity, efficiency, and overall performance of your system. Two of the most commonly used materials in the industry are High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). Both materials have their unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the detailed comparison between HDPE and PVC pipes, focusing on their properties, applications, and suitability for various projects.
Introduction to HDPE and PVC Pipes
HDPE Pipes
HDPE pipes are highly flexible and can bend without breaking, making them extremely adaptable to various installation environments. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in areas prone to ground movement, seismic activities, or where the pipes need to navigate around obstacles. HDPE’s ability to flex under pressure also means it can withstand significant impact forces without cracking or breaking.
PVC Pipes
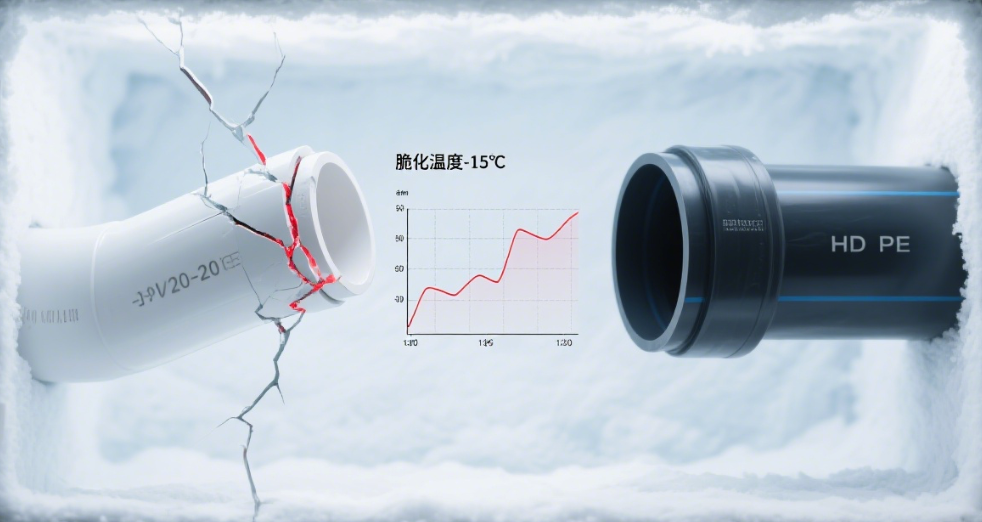
PVC pipes are rigid and brittle, especially in cold temperatures, which makes them more prone to cracking under impact. While PVC is known for its structural strength, its rigidity can be a disadvantage in environments where ground movement or heavy loads are common. In cold climates, PVC pipes can become even more brittle, increasing the risk of cracking and failure. This is a significant consideration for applications such as outdoor irrigation systems or in regions with frequent seismic activity.

Comparative Analysis of HDPE and PVC Pipes
Physical Properties
HDPE pipes are highly flexible and can withstand significant bending without cracking. This property makes them ideal for applications where the pipes need to navigate around obstacles or conform to uneven terrain. HDPE’s flexibility also reduces the need for additional fittings, saving time and cost during installation. In contrast, PVC pipes are rigid and less flexible, making them more suitable for straight runs and applications where rigidity is required.
When it comes to impact resistance, HDPE pipes outperform PVC pipes. HDPE’s high impact strength makes it more resistant to damage from external forces, such as heavy loads or ground movement. PVC pipes, while strong, are more brittle and prone to cracking under extreme conditions. This difference in impact resistance is particularly important in applications where the pipes are exposed to harsh environmental conditions or heavy loads.
UV resistance is an important consideration for pipes that will be exposed to sunlight. HDPE pipes are highly resistant to UV radiation, ensuring they do not degrade when exposed to sunlight over extended periods. This makes HDPE pipes suitable for outdoor applications, such as irrigation systems or exposed pipelines. PVC pipes, however, are more susceptible to UV degradation, which can lead to brittleness and cracking over time. While UV-resistant coatings can be applied to PVC pipes, this adds an additional layer of maintenance and cost.
Applications
HDPE
HDPE pipes are used in a variety of applications due to their unique combination of properties. Some of the most common applications include:
Water Supply Systems: HDPE pipes are ideal for high-pressure water supply systems due to their strength and durability. They can handle significant water flow rates and pressure surges, ensuring a reliable supply of water.
Wastewater Management: HDPE pipes are highly resistant to chemical degradation, making them suitable for wastewater systems. They can withstand the corrosive nature of wastewater and ensure a long service life.
Gas Distribution: HDPE pipes are commonly used in natural gas distribution systems due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They can be easily installed and are highly reliable.
Irrigation Systems: HDPE pipes are used in agricultural irrigation systems due to their flexibility, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. They can be easily maneuvered to fit the contours of the land.
Drainage Systems: HDPE pipes are used for stormwater and sewage drainage systems due to their ability to handle high flow rates and resist corrosion.
PVC
PVC pipes are used in a wide range of applications due to their affordability, ease of installation, and durability. Some of the most common applications include:
Residential and Commercial Plumbing: PVC pipes are widely used in residential and commercial buildings for water supply lines, drainage systems, and irrigation. They are cost-effective and easy to install, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Drainage Systems: PVC pipes are commonly used for domestic drainage and sewage systems due to their smooth interior surface and resistance to corrosion. They ensure efficient water flow and reduce the risk of blockages.
Irrigation Systems: PVC pipes are used in small-scale irrigation systems due to their affordability and ease of installation. They can be easily maneuvered and installed in various configurations to meet the needs of different agricultural applications.
Electrical Conduits: PVC pipes are used as electrical conduits due to their insulating properties and resistance to corrosion. They protect electrical wiring from moisture and other environmental factors, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.

Installation and Maintenance
HDPE pipes are typically joined using Heat or electric melting, which creates a seamless, leak-free connection. This method ensures the pipes can withstand ground movement and other external forces without the risk of leakage. The long service life of HDPE pipes, combined with their low maintenance requirements, makes them a cost-effective choice in the long run. HDPE pipes are also highly resistant to corrosion and UV degradation, reducing the need for protective coatings and other treatments.
PVC pipes are usually joined using solvent cement or bell and spigot joints. While these methods are relatively simple and cost-effective, they can be prone to leakage and other issues over time. PVC pipes also require periodic inspection to ensure the integrity of the joints, particularly in applications where the pipes are exposed to harsh environmental conditions or heavy loads. To shield PVC pipes from UV degradation in outdoor use, UV-resistant stabilizers—typically carbon black or specialized UV absorbers—are incorporated during production, creating an integral protective layer that blocks harmful rays and prolongs service life.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
HDPE
Manufactured with Lower Embodied Energy:
HDPE is produced using a relatively energy-efficient process compared to many other materials. This lower embodied energy means that the production of HDPE pipes has a smaller carbon footprint, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. This is particularly important in the context of global efforts to mitigate climate change and promote sustainable practices.
Recyclable into Pipes or Other PE Products:
HDPE is highly recyclable and can be reprocessed multiple times without significant loss of quality. This makes it an ideal material for circular economy initiatives, where waste materials are repurposed to create new products. Recycled HDPE can be used to manufacture new pipes or other plastic products, reducing the need for virgin materials and conserving natural resources. Akan Enterprise Group (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. actively supports recycling initiatives and ensures that its HDPE products are designed with recyclability in mind.
Non-Toxic and Does Not Leach Harmful Chemicals:
HDPE is a non-toxic material that does not leach harmful chemicals into the environment or the water it carries. This makes HDPE pipes safe for use in potable water systems, ensuring that the water supply remains uncontaminated. The non-toxic nature of HDPE also means that it is safe for use in agricultural and environmental applications, where the risk of chemical leaching is a significant concern.
Leak-Free Joints Reduce Water Loss in Distribution Systems:
The use of heat fusion to join HDPE pipes creates seamless, leak-free connections. This reduces the risk of water loss in distribution systems, which is a critical consideration for water utilities aiming to conserve water and reduce operational costs. Leak-free joints also mean that HDPE pipes are less likely to fail over time, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting system.
PVC
Recyclable but Requires Controlled Processes:
While PVC is technically recyclable, the process is more complex and requires controlled conditions to ensure the material is properly processed. This complexity can limit the feasibility of large-scale recycling efforts, particularly in regions where recycling infrastructure is not well-developed. Proper recycling of PVC requires careful handling and processing to avoid contamination and ensure the material can be effectively repurposed.
Manufacturing Involves Chlorine, Raising Environmental Considerations:
The production of PVC involves the use of chlorine, which can raise environmental concerns. Chlorine-based processes can result in the release of harmful by-products, such as dioxins, which are toxic and persistent in the environment. While modern PVC manufacturing processes have significantly reduced these emissions, the potential environmental impact remains a consideration for some applications.
Stable During Use but Must Be Disposed of Responsibly to Avoid Environmental Impact:
PVC pipes are stable and durable during their service life, but their disposal requires careful consideration. PVC is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment if not properly managed. Responsible disposal methods, such as recycling or controlled landfilling, are essential to minimize the environmental impact of PVC products at the end of their life cycle.
With increasing global focus on sustainability, HDPE often aligns better with green infrastructure initiatives, although PVC remains widely used due to cost benefits and simplicity. The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility is driving many industries to prioritize materials with lower environmental impact. HDPE’s recyclability, lower embodied energy, and non-toxic nature make it a preferred choice for green infrastructure projects. However, PVC continues to be widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, particularly in applications where these factors are prioritized over environmental considerations.
Lifecycle Costs and Maintenance
HDPE
Higher Initial Material Cost but Lower Installation and Maintenance Costs Due to Leak-Free Joints and Flexibility:
While HDPE pipes may have a higher initial material cost compared to PVC, the overall lifecycle cost is often lower. The flexibility of HDPE pipes allows for easier installation, reducing labor costs and installation time. The use of heat fusion to create leak-free joints means that HDPE systems are less likely to require maintenance or repairs due to leaks. This results in lower maintenance costs over the life of the system.
Longer Lifespan Reduces Replacement Cycles:
HDPE pipes have a long service life, often exceeding 50 years with proper installation and maintenance. This extended lifespan means that HDPE pipes require fewer replacements over time, reducing the overall cost of the system. The durability and resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation ensure that HDPE pipes remain reliable and efficient throughout their service life.
Lower Water Loss Translates into Operational Savings for Water Utilities:
The leak-free nature of HDPE joints reduces water loss in distribution systems, which is a significant advantage for water utilities. Reducing water loss not only conserves a valuable resource but also translates into operational savings by reducing the amount of water that needs to be treated and distributed. This efficiency can result in significant cost savings over the life of the system.
PVC
Lower Initial Cost:
PVC pipes are generally less expensive than HDPE pipes, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. The lower initial cost can be a significant factor in applications where cost is a primary consideration.
Potential Maintenance Costs Due to Joint Leaks Over Time:
While PVC pipes are durable and low maintenance, they are more prone to leaks at the joints over time. Solvent cemented joints or rubber ring joints can fail if not properly installed or if subjected to significant movement or pressure changes. This can result in maintenance costs over the life of the system, particularly in applications where leaks can cause significant damage or disruption.
Brittle Failure in Cold Climates May Require Section Replacements:
PVC pipes can become brittle in cold climates, increasing the risk of cracking and failure. This can result in the need for section replacements, particularly in regions with frequent freezing temperatures. The potential for brittle failure means that additional maintenance and inspection may be required to ensure the integrity of the system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the main differences between HDPE and PVC pipes?
A1: HDPE pipes are highly flexible, durable, and resistant to chemicals and UV radiation, making them suitable for high-pressure and demanding applications. PVC pipes are rigid, cost-effective, and easy to install, making them ideal for low to moderate pressure applications.
Q2: Which material is better for water supply systems?
A2: HDPE is better for high-pressure water supply systems due to its flexibility, durability, and resistance to pressure surges. PVC is suitable for low-pressure water supply systems where cost is a primary consideration.
Q3: Are HDPE and PVC pipes recyclable?
A3: Yes, both HDPE and PVC pipes are recyclable. However, HDPE is more widely recycled and has a simpler recycling process. PVC recycling is more complex and requires controlled processes.
Q4: Which material is more suitable for gas distribution systems?
A4: HDPE is preferred for gas distribution systems due to its flexibility, durability, and resistance to corrosion and environmental stress cracking.
Q5: Can PVC pipes be used in cold climates?
A5: PVC pipes can be used in cold climates, but they become more brittle and prone to cracking. HDPE pipes are more resistant to cold temperatures and are less likely to crack.
Conclusion
Choosing between HDPE and PVC pipes depends on the specific requirements of your project. HDPE pipes are ideal for high-pressure,, applications where flexibility and durability are crucial. They offer long-term cost savings and are highly sustainable. PVC pipes are a cost-effective choice for low to moderate pressure applications and are easy to install.
Related Articles

Can HDPE be used for drainage?
Effective drainage systems are essential for managing stormwater runoff, sewage, and wastewater in both urban and rural settings. This article explores the suitability of HDPE pipes for drainage systems, focusing on their unique advantages, real - world applications, and how they compare to traditional materials. Learn how HDPE pipes from Akan Enterprise Group (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. provide a durable, flexible, and environmentally friendly solution for modern drainage needs.
CONTACT
Get in Touch With Us


